Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way businesses operate across various industries. Forward-thinking companies are exploring how blockchain can help optimize processes, engage customers, and unlock new revenue streams. However, successfully integrating blockchain requires a strategic, long-term approach. This article provides a framework for developing comprehensive blockchain business strategies.
Blockchain is essentially a distributed database that permanently records transactions in a way that makes them tamper-resistant. The records or blocks are linked using cryptography and updated by consensus among the nodes participating in the system. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
For a blockchain to work decentralized consensus must be reached regarding the ordering and verification of transactions. This is achieved through various protocols like PoW or PoS. Every full node maintains a copy of the blockchain which serves as a single source of truth regarding the asset transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Blockchain can help streamline business processes and reduce costs by cutting out middlemen and unnecessary intermediaries. It brings trust, transparency, and immutability to business transactions by maintaining an immutable record of transactions. This improves auditability, reduces risks of errors and fraud.
Smart contracts on blockchain enable automation of business processes and contracts. This increases efficiency. Traceability improved by blockchain can help manage compliance and meet regulatory requirements for industries like food, pharmaceutical etc. Secure authentication using blockchain can improve customer experience and security of transactions and data sharing between businesses and customers.
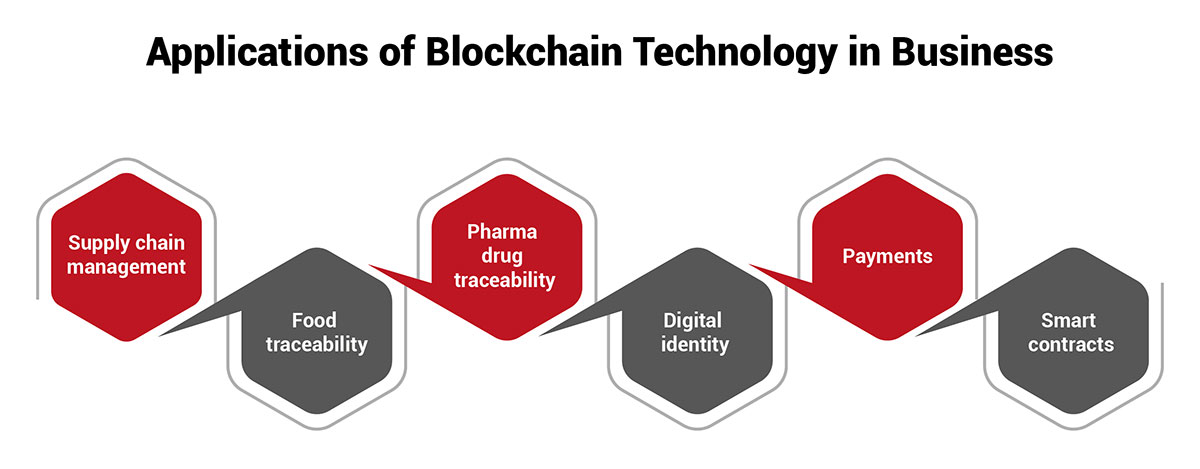
Here are some blockchain applications for businesses:
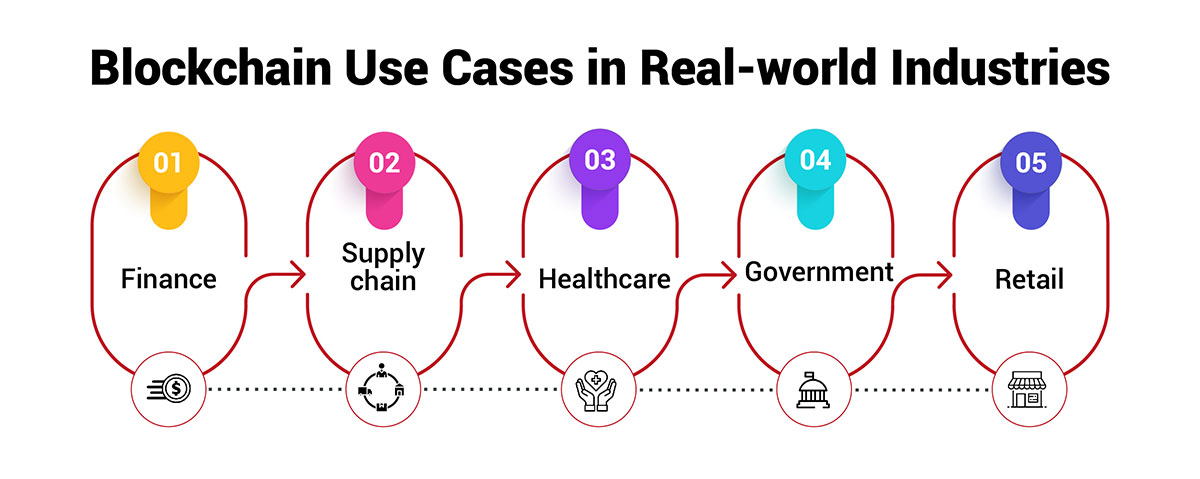
Blockchain technology is finding myriad applications across several industries as businesses recognize its potential to streamline processes, enhance transparency and protect sensitive information. Some prominent use cases of blockchain in real-world sectors include finance, supply chain, healthcare, government and retail.
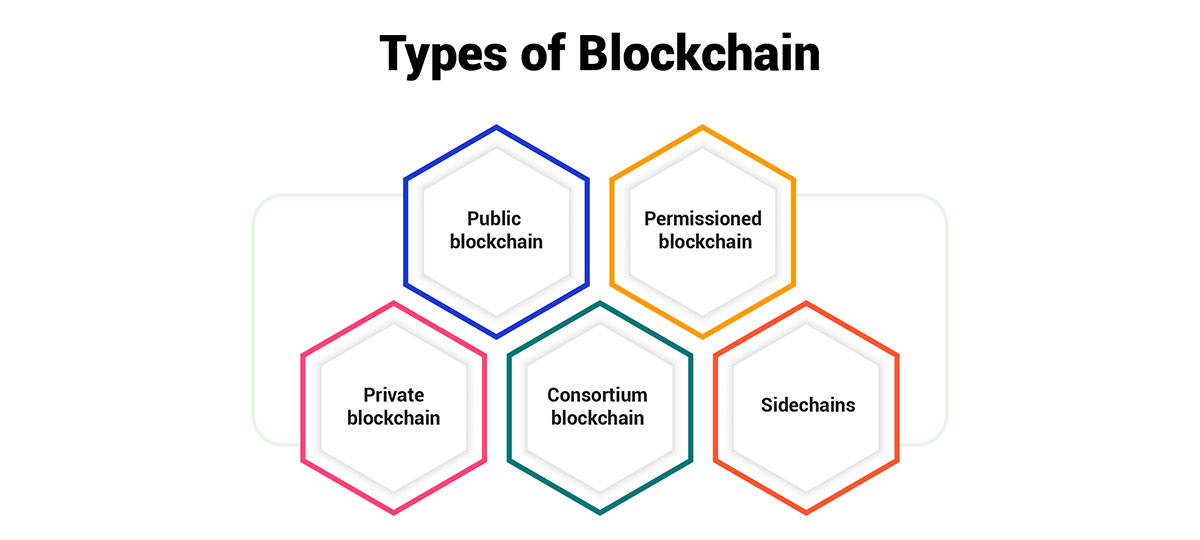
The main types of blockchain are:
Here are some steps to integrate blockchain technology into your operations through strategic planning.
1. Understanding Blockchain Technology
The first step is gaining a thorough understanding of blockchain and how it works. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that can record transactions across a peer-to-peer network. It allows for the secure, transparent validation, and verification of transactions without a central authority.
There are two main types of blockchain - public and private. A public blockchain like Bitcoin is fully decentralized, permissionless, and allows anyone to participate. A private blockchain offers greater control, as access and validation is restricted to approved partners or consortium members. Choosing between these models is an important strategy consideration.
Blockchain capabilities like smart contracts, tokenization, and decentralized apps (DApps) also enable innovative new business and operating models. Smart contracts are self-executing codes that facilitate automatic transactions. Tokens represent real or virtual assets that can power new economies. DApps deliver services on blockchain networks in areas like finance, logistics and more.
2. Assess Your Business Needs and Opportunities
The next step is a thorough assessment of how blockchain could benefit your specific business. Start by identifying pain points in existing processes like latency, lack of transparency or single points of failure. Also, examine new opportunities presented by emerging technologies and changing customer expectations.
Map out your end-to-end value chain to pinpoint areas that could be optimized using blockchain attributes like enhanced security, traceability and automatic execution. For example, blockchain could streamline supply chain management, simplify cross-border payments, power innovative loyalty programs or enable new frictionless digital marketplaces.
Consider use cases across different departments too - finance for more efficient settlements, HR for credentialing, marketing for engaging personalized experiences, and product development for IoT applications. Benchmark competitors already integrating blockchain to future-proof your strategy.
3. Designing Your Blockchain Ecosystem
With target opportunities identified, outline the design of your initial blockchain ecosystem. Start small and select one high-impact use case to pilot as overdesign could impact adoption.
Specify technical requirements like data architecture, consensus protocol, and infrastructure needs. Choose appropriate blockchain type - a permissioned chain may suit tightly-controlled B2B networks while decentralized solutions could power open ecosystems.
Identify key participants and their on-chain roles. For example, in supply chain traceability, producers, distributors, logistics firms, and retailers need unique capabilities. Define governance standards covering compliance, upgrades, and dispute resolution.
Build a prototype on testnets to refine UX, assess scalability and debug. Partnering with blockchain specialists during the design and development stages reduces risks. Gradually expanding the ecosystem by incorporating new use cases and participants creates a sustainable network effect.
4. Crafting Your Business Model
Developing a viable business model is critical for blockchain initiatives to gain executive support and funding. Identify revenue streams, key activities, resources required, and partnerships needed to deliver value. Standard models like SaaS or transaction fees may not always apply.
Innovative token-based models are gaining traction. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) can power new creator economies. Utility tokens with inherent use-case value rather than speculative assets spark true tokenomics. Security tokens representing real-world assets generate new capital market opportunities.
Well-designed token incentives and redistribution mechanisms encourage community participation. Consider regulatory compliance needs upfront. New partnerships could open new markets - for example, a media major tapping a creator network. Quantifying expected ROI and timeframe helps secure buy-in for long-term investments.
5. Implementing Your Strategy
With planning complete, the focus shifts to executing the blockchain business strategy. Establish a center of excellence to drive change, invest in developer talent, and educate employees. Change management is critical to overcome internal resistance.
Integrate the initial use case while continuing design for expansion. Transparent communication and performance tracking boost adoption. Proper testing with early partners finds bugs before public launch. Partner enablement toolkits simplify participation.
Constant iteration and refinement based on user feedback keeps the ecosystem relevant. Consider token launches and events as engagement tools. Extend the network through partners over time. Compliment technology with traditional channels to reach target markets.
Establish objective metrics to monitor impacts on KPIs regularly. Course-correct strategy based on data. Leverage successes to gain executive sponsorship of ambitious, transformative ideas. Over time, blockchain can fundamentally change business and operating models.
By following a thoughtful, phased approach - from assessing opportunities to designing technical frameworks to outlining business models - companies can harness blockchain's potential for competitive advantage. Successful strategies view blockchain holistically while focusing initially on high-impact use cases. Continuous learning, iteration, and community participation drive long-term, sustainable value from this emerging technology.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.