Strategy Maps: Understanding & Crafting Your Blueprint for Business Plans
 March 08, 2024
March 08, 2024
Clear communication of strategy is vital for organizations to effectively execute their plans. Without a comprehensive understanding of their goals and priorities, how can they expect successful implementation?
Enter the strategy map – a fail-safe mechanism guiding organizations through their strategic objectives in a logical sequence. In this blog, we’ll understand a strategy map and its uses, and explore the steps required to craft a perfect map for your next business plan.
What is a Strategy Map?
A strategy map is a highly effective strategic planning tool used to visually represent an organization's entire strategy on a single sheet of paper. An effective strategy map should include:
-
Cause-and-Effect Relationships: Arrows indicate the interconnectedness between various value objectives, highlighting the sequence of actions necessary to achieve strategic goals.
-
Action-Oriented Goals: Goals expressed using action verbs, depicting the specific outcomes or achievements your organization aims for.
The primary purpose is to communicate how your business intends to create value, complemented by a balanced scorecard—a tool designed to monitor and evaluate non-financial variables within your organization.
Why Strategy Maps matter in Business Strategy
Utilizing a strategy map is very important for organizational growth. Here’s why a strategy map matters:
Understanding Goals:
-
Clarity of Objectives: A strategy map clarifies the company's goals and their interrelations, simplifying comprehension for all stakeholders.
-
Performance Monitoring: It offers a straightforward overview of the organization's performance concerning its primary strategic objectives, aiding in timely adjustments.
Strategy Development:
-
Strategic Visualization: Creating a strategy map aids in visualizing how various goals, such as financial targets, align with internal processes and learning and growth objectives.
-
Collaborative Planning: Teams can strategize collectively on achieving these goals by understanding their interconnectedness.
Evaluating Progress:
-
Regular Assessment: Strategy maps facilitate the regular evaluation of progress towards goals, enabling teams to track advancements and identify areas for improvement.
-
Dynamic Updates: Regularly refreshing the strategy map to reflect progress ensures a continuous assessment of the organization's performance against its crucial objectives.
Eight Steps to Develop a Strategy Map
Crafting a strategy map is a methodical process that transforms organizational aspirations into actionable business plans. Let's explore each step:
-
Step 1: Define Mission and Vision
It is always important to begin by encapsulating the core purpose and direction of a business plan. This offers a concise depiction of the organization's short and long-term objectives, providing a glimpse into its future— serving as the bedrock for the strategy map.
-
Step 2: Evaluate Your Company's Present Performance
To continue forward in your strategy, conduct a comprehensive analysis of the organizational landscape, delving into industry trends and stakeholder dynamics. Understand your company's existing strengths and weaknesses and pinpoint areas for improvement. By identifying challenges within your company, you'll gain valuable insights into factors that may have slowed its growth, enabling you to devise strategies to mitigate these obstacles.
-
Step 3: Define the Strategy
After conducting a comprehensive evaluation, it's imperative to develop a robust strategy that aligns closely with the organization's mission. The key emphasis should be on initiatives aimed at establishing sustainable competitive advantages, such as providing superior value to customers or optimizing internal processes. It's important to bear in mind that strategic clarity is essential for ensuring coherence and direction in organizational pursuits.
-
Step 4: Consider Your Company's Processes and Growth
Once you've outlined your steps, it's essential to assess how each team can contribute and grow to ensure the successful completion of each stage. This development encompasses both the refinement of the company's internal work processes and the growth of individuals through knowledge acquisition and training. To enhance productivity and efficiency, teams may need to engage in additional research or implement new practices to establish a robust foundation for executing the new strategies.
-
Step 5: Translate the Strategy
Next comes the crucial step of translating the strategic vision into a tangible framework through a business strategy map. By employing a balanced scorecard approach, objectives can be delineated across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth (discussed later).
-
Step 6: Highlight Cause and Effect Relationships
It is crucial to establish causal relationships between objectives within each perspective, elucidating how the achievement of one goal influences others. This interconnectedness highlights the holistic nature of the strategy, guiding coherent decision-making and resource allocation.
-
Step 7: Revisit and Revise the Strategy Map
Lastly, it is important to continuously revisit the strategy map as you reach milestones. Since the map typically encompasses broad, ambitious company objectives, achieving them may span months or even years. Regularly check the map as you progress and be prepared to revise the strategy map as needed. This ensures that your strategy remains adaptable and responsive to evolving circumstances.
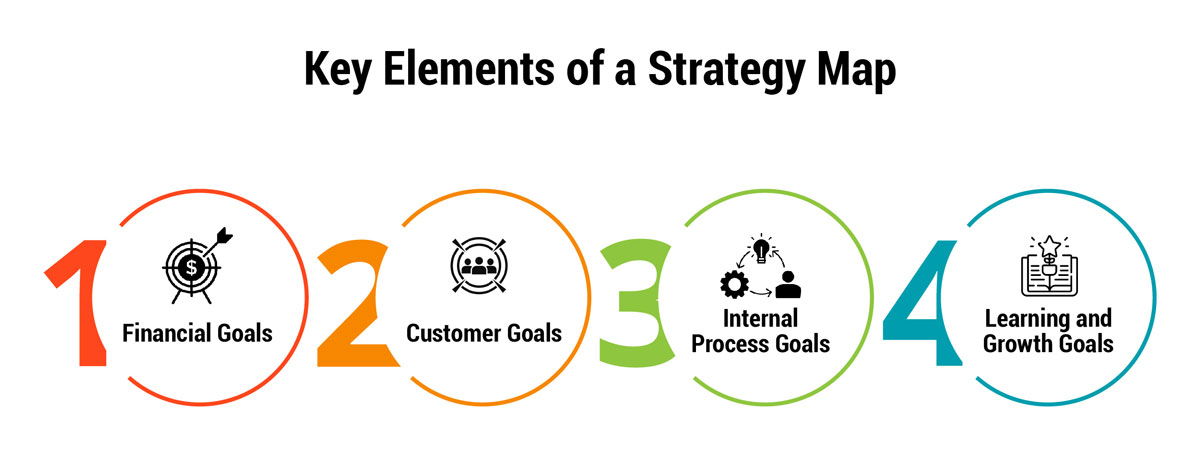
What to Include in a Strategy Map? The Key Elements
A strategy map typically has four primary elements, each tailored to reflect the organization's specific priorities and objectives. Here's a breakdown of these essential key elements:
-
Financial Goals: Positioned prominently, financial goals often occupy the top row of a strategy map. As a driving force for businesses, these goals focus on the business plan related to increasing profits, revenue growth, cost reduction, or achieving specific financial targets.
-
Customer Goals: Customer goals underscore the importance of keeping customers satisfied and loyal. This section may vary in name depending on the nature of the organization (e.g., clients or patients instead of customers), but its core focus remains on fulfilling customer needs.
-
Internal Process Goals: These goals are directly linked to enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing workflow, and improving performance in areas critical to achieving financial and customer-related outcomes.
-
Learning and Growth Goals: Located towards the bottom of the strategy map, these goals aim to foster continuous improvement and innovation by investing in employee training, skill development, and knowledge enhancement.
Benefits and Importance of Strategy Maps
Strategy maps play a pivotal role in the success of businesses by serving as essential tools for:
-
Aligning Business Processes with Goals: Business strategy maps visually represent the connection between strategic objectives and day-to-day operations, ensuring that every action taken within the organization contributes to its overarching goals.
-
Unifying Objectives Across All Company Levels: By providing a clear visual representation of goals and processes, strategy maps facilitate a shared understanding of the strategic direction among leaders and employees at all levels of the organization.
-
Fostering Teamwork and Collaboration: These maps illustrate how individual roles and tasks contribute to larger organizational goals, fostering teamwork, and collaboration by enhancing employees' understanding of their impact on the organization's success.
-
Enabling Intentional Goal Setting and Actionable Steps: Strategy maps translate broad organizational goals into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives, providing a roadmap for actionable steps needed to achieve success.
-
Increasing Organizational Involvement and Cross-Functional Awareness: Strategy maps span across all departments and areas of the organization, ensuring that everyone is aligned with and actively contributing to the organizational objectives. This increases employee engagement and fosters cross-functional awareness.
-
Empowering Employees with Clear Role Understanding:
By outlining specific objectives and the role of each department or individual in achieving them, strategy maps empower employees with a clear understanding of their roles, responsibilities, and contributions to the organization's mission.
-
Facilitating Better Risk Management Through Informed Decision-Making: These maps encourage thorough consideration of objectives from every angle, leading to better risk management by ensuring that decisions are made with a clear understanding of their potential impact on the organization's success.
How to Align Business Goals with Organizational Strategy Using a Strategy Map?
Here are essential steps to achieve alignment:
-
Breakdown of Overall Strategy
You must divide the organization's overall strategy map into smaller, more specific goals and objectives that can be assigned to different teams.
-
Initiative Development
It is necessary to develop specific initiatives and action plans directly supporting each team's assigned goals and objectives, ensuring alignment with the organization's overarching strategy.
-
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
You should carefully identify key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards each team's goals and objectives. Ensure these KPIs are aligned with the organization's overall KPIs for comprehensive performance tracking.
-
Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Next comes establishing clear roles and responsibilities for team members that directly support the team's goals and objectives. It is imperative to define specific tasks and responsibilities necessary to achieve these goals and objectives effectively.
End Note
Crafting a strategy map is essential for aligning your organizational goals and directing decision-making throughout the strategy execution process. Business strategy mapping facilitates more deliberate and strategic decision-making, enhances organizational engagement, promotes cross-functional awareness, and strengthens risk management practices.


