Aligning an organization is crucial yet challenging, especially amid ongoing changes. One strategic tool businesses use to manage complexity and drive consistent alignment is the McKinsey 7-S Model.
Learn how leaders leverage the Mckinsey 7-S model - a strategic framework analyzing structure, strategy, systems, skills, staff, style and shared values - to diagnose gaps, guide transformations, and improve organizational effectiveness.
In this article, we explore the 7-S framework, its implementation, and how leaders have leveraged this model to direct effective transformations.
The McKinsey 7-S Model is a change management strategy framework that analyzes a company's organizational design to help leaders effectively manage organizational change. It does this by looking at the interactions and alignment between seven key interconnected elements that influence an organization's ability to change:
The model proposes that these seven elements influence each other, like a domino effect. The central placement of shared values indicates its crucial role - a strong, healthy culture impacts all other elements and drives change. Leaders must get the shared values and culture right to enable organizational change.
McKinsey's model comprises seven elements in two categories:
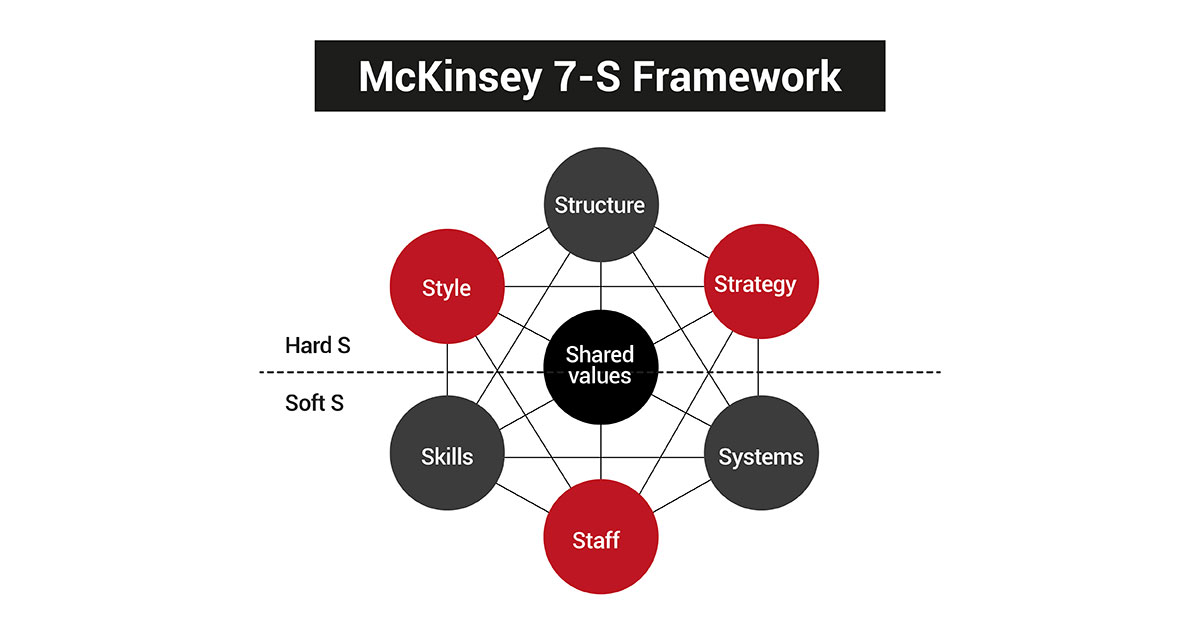
Hard Elements: More tangible elements that leadership and management can directly influence.
Soft Elements: Intangible, culture-driven elements.
The hard elements are more easily identified and adjustable. However, the model proposes soft elements are equally crucial for organizations to examine and realign to drive successful change.
Leaders can effectively implement the model using a top-down approach:
The first step is to conduct an analysis of the current state of the organization across the 7-S dimensions. The goal is to spot inconsistencies, misalignments, and areas needing change.
This involves thoroughly evaluating the organization's:
Compare findings to identify gaps between current and desired states per element and in their interactions. List out unaligned processes and practices needing realignment.
Conduct employee surveys, workflow analysis, and leadership discussions to gather broad insights into potential issues. Identify pain points experienced by various stakeholders.
Next, research extensively to define what the optimal organizational design should be to enable business strategy execution.
Take into account your long-term business vision and priorities when deciding what changes different 7-S elements require. Consult strategic experts to benchmark against organizational best practices. Importantly, the "ideal state" vision must align with leadership aspirations as well as wider team sentiments. Achieve this balance through change management surveys and focus group discussions.
The outcome of this step should be clarity on the required realignments per element - like flatter hierarchy, upgraded tech systems, better incentives, etc.
With the gaps identified and ideal state chartered, the next step is creating a detailed change implementation roadmap.
Define the precise hierarchy changes, communication protocols, system upgrades, training programs, and policy changes required to shift the organizational design. Include specific departments impacted and resources needed.
Assign change sponsors and owners for accountability. Set targets and timelines for various initiatives outlined in the plan. Creating this plan collaboratively, with leadership and employee inputs incorporated, will drive engagement and momentum.
The most crucial step is the actual change implementation based on the action plan. Careful execution avoids resistance, confusion, and failures.
Appoint internal change agents from impacted teams or hire external consultants skilled in organizational change management best practices. Conduct regular training workshops. Offer communication forums for clarity. Encourage employee participation at every step, from feedback to pilots. Leadership alignment on the "why" and support during transitions is vital. Celebrate small wins through the process.
As organizational elements and market dynamics constantly shift, it's key to sustain momentum post-implementation with rigorous review mechanisms.
Set up processes to continually track interdependencies between the 7-S elements - like skills and staff or systems and structure. Check that realignments made enable strategy delivery consistently. Adapt action plans if critical misalignments re-emerge. Use insights to refine change initiatives or maintain competitive edge through new transformations.
The McKinsey 7-S model framework offers a simple yet effective method for leaders to analyze and enhance organizational design. Following this step-by-step implementation methodology can help companies execute complex change initiatives smoothly.
The focus should be on identifying gaps, correcting course, sustaining alignment, and repeating the process as new market realities emerge. With constant assessment and adaptation, companies can build resilient systems powered for high performance.
Here is a detailed explanation of two McKinsey 7-S model examples:
Nokia's journey from being an industry pioneer to losing significant market share and eventually getting acquired by Microsoft aligns well with the McKinsey 7-S model analysis of change failure.
Strategy Dilemma: Nokia faced a dilemma regarding whether to optimize costs and volumes, enhance device performance, or maximize security. They opted for a cost-leadership approach but failed miserably on innovation and device performance fronts.
Structure: Nokia had a hierarchical, top-down organizational structure where employees were working in silos with limited communication across teams. To compete with the likes of Apple, Nokia should have transitioned to a more agile, decentralized structure with increased collaboration.
Systems: Nokia considered organizational agility and being nimble as its key competitive advantages in the past. With a skilled engineering workforce, Nokia initially was in a strong position to rapidly innovate its products and increase operational efficiency.
Skills: Nokia had built a large pool of highly skilled telecom engineers over the years and leveraged that to design highly efficient mobile phones earlier on. Lack of relevant skills was not an initial gap that led to their downfall.
Staff: Surprisingly, Nokia removed the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) position from top management during 2007-2010 (Source: BrandMinds.com). This led to extremely high attrition rates of engineers and technology executives. New hires also weren't adequately skilled to start with, eventually causing the downfall of Nokia as a cutting-edge mobile brand.
Style: Due to the low technical competence of leaders appointed, employee morale was generally low during Nokia's decline. Instead of bringing in people with relevant backgrounds to further innovation and business growth, Nokia clearly needed transformational, visionary change leadership during that period to rejuvenate technology advancement and cutting-edge product designs.
Shared Values: The core values of the company previously enabling business performance were Respect, Achievement, Renewal and Challenge. However, these got diluted among competing priorities.
In contrast, here is how the global fast-food giant McDonald's successfully leverages the McKinsey 7-S model components to continually drive organizational change and evolution:
Strategy: McDonald's gains significant market share through adopting a cost-leadership approach. The company also sets clear, time-bound SMART goals to achieve both long-term strategic vision as well as short-term objectives.
Structure: Unlike other complex multinational corporations, McDonald's has a relatively flat organizational structure where a store manager efficiently manages restaurant employees. Store crews function as close-knit teams and can easily access senior management when required.
Systems: McDonald's is known for constantly innovating various systems to reduce customer wait times and make restaurant operations along with the whole supply chain more efficient. Some examples are mobile ordering apps, self-ordering kiosks, delivery partnerships, lean kitchen processes etc.
Shared Values: Values like integrity, serving diverse customer demographics, hiring employees from different backgrounds, encouraging teamwork and giving back to communities shape McDonald's operations. These are reflected in the core values - Serve, Inclusion, Integrity, Community and Family.
Style: McDonald's leverages a highly participative leadership style where senior leaders actively engage with employees at different levels to seek frequent feedback to improve policies, operations and resolve conflicts.
Staff: With over 150,000 employees globally, McDonald's is one of the largest employers worldwide (Source: Wikipedia.org). The company firmly believes in diversity and strives to enable employee satisfaction through various initiatives.
Skills Training: McDonald's regularly trains employees through real-world simulations to provide an excellent customer experience and handle objections effectively. This focus results in highly skilled staff.
In summary, the 7S model offers business leaders a framework to analyze how integral organizational elements impact each other. As the Nokia and McDonald's examples illustrate, leveraging 7-S insights properly can drive change or hindrance.
In conclusion, the McKinsey 7-S model offers a framework for organizations to analyze alignment and enable success. Leaders can assess interdependencies between these components to pinpoint organizational gaps or misalignments. Addressing these effectively guides strategic improvements and change initiatives.
With robust research and committed implementation, the McKinsey 7-S model gives organizations a holistic blueprint towards increased alignment and competitiveness. Continuous assessment between elements helps firms execute their vision.
The framework offers a simple, structured methodology to diagnose issues and track progress. Ultimately, organizations aiming for agility, innovation or growth can leverage the 7-S model to reach higher performance excellence.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.