Gaining a competitive edge is crucial for business success. But with rivals constantly looking to get ahead, how can you make sure your organization sustains its advantage? The answer lies in identifying unique resources that set you apart.
This is where VRIO analysis comes in.
VRIO is an internal assessment tool that helps companies determine if they have resources and capabilities that provide strategic competitive advantages. Unlike a simple list of strengths, VRIO focuses on sustainable advantages—ones difficult for competitors to imitate. In this article, we’ll explore:
Let’s start with understanding what VRIO is and why it’s so vital to strategic planning.
Coined by Jay Barney in 1991, VRIO stands for Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization—the 4 questions used to assess a company’s internal resources. Through this analysis process, organizations can determine if they have capabilities that provide real, long-lasting competitive advantages in the market.
Instead of relying on a random assortment of strengths, VRIO helps businesses strategically focus their efforts on excelling in key areas to stay ahead.
Incorporating VRIO analysis into the strategic planning process is critical for several key reasons:
The very purpose of VRIO is to pinpoint a company's rare and costly-to-imitate resources that can drive strategic growth. By evaluating resources against the VRIO criteria of value, rarity, inimitability, and organization, businesses gain insight into their unique strengths and capabilities that set them apart. Resources meeting all VRIO criteria have the potential to become sustained competitive advantages. Identifying these crown jewel assets through VRIO assessment provides focus for business strategy formulation and decision making.
Every organization has limited budgets and capacity. VRIO analysis helps businesses understand where resources should be targeted to maximize returns. Assessing each resource's potential strategic value guides optimal investment and capital allocation decisions. Resources demonstrating value, rareness and inimitability deserve priority funding and talent investment since they offer the greatest competitive differentiation. On the other hand, resources not meeting VRIO criteria should receive fewer resources.
By revealing rare and costly-to-imitate resources, VRIO highlights an organization's core competencies - what it does best. These differentiating capabilities and strengths should be at the heart of strategic plans. VRIO analysis helps businesses define their core competencies and craft strategies that fully leverage them through new initiatives, market approaches and partnerships. Building strategy on proven organizational abilities provides confidence in execution.
Strategy development involves making decisions about markets, investments and business priorities. VRIO analysis guides and focuses an organization's strategy by providing critical insights into internal resource strengths and weaknesses. Resources meeting all VRIO criteria signal strategic priorities and opportunities, while vulnerabilities are revealed through resources lacking aspects of VRIO. With this clarity, strategic plans can be sharpened around a company's areas of greatest promise and advantage.
Expanding into new markets or products carries risk. VRIO assessment provides input on how well internal resources and competencies can be transferred to new areas, versus needing wholly new capabilities. Highly valuable and rare resources that could confer advantage in related or emerging spaces may indicate opportunities worthy of diversified investment, while low VRIO resources suggest expansion barriers.
VRIO provides a structured, objective business model for evaluating a company's resources versus simple lists of strengths or capabilities. By forcing discipline around the four VRIO criteria, subjective assessments are minimized. The tangible VRIO analysis can then directly input into strategic discussions, keeping planning dialogue fact-based.
Now that we know what VRIO is, let’s break down each element and why it matters:
The first and most fundamental criteria in the VRIO framework is determining if a resource or capability adds value. Value refers to whether the resource helps the company improve efficiency, effectiveness, or overall performance in a way that creates competitive advantage.
Resources that provide value allow organizations to better meet customer needs, enhance operations, reduce costs, boost quality, align with strategic objectives, or capitalize on market opportunities. Value also means that the resource helps neutralize external threats. Essentially, value provides the foundation for competitive advantage - without it, sustainability is not possible.
When assessing the value of an internal resource or capability, ask critical questions like:
If the answer is yes to questions like these, the resource likely creates value. This value directly translates to improved organizational and financial performance.
After determining value, the next vital step is assessing rarity. A valuable resource only leads to a competitive advantage if it's rare and not widely possessed by competitors.
Rarity means that only a small number of competing firms have access to this valuable resource or capability. It's the scarcity that makes it meaningful from a strategic perspective. If the resource is common across the industry, it may be best practice but does not differentiate an organization.
When evaluating rarity, gathering competitive intelligence is key. Research which rivals have access to similar resources and capabilities. If only one or two competitors possess something of value, it meets the rarity criteria.
Examples of rare resources include proprietary technology, unique partnerships/distribution channels, protected intellectual property, specialty ingredient sourcing, and highly-skilled talent.
The third facet of VRIO analysis examines imitability - how easy or difficult it is for competitors to replicate or substitute something of value. Sustainable competitive advantage depends heavily on rivals not being able to duplicate the resource that differentiates an organization.
Several key factors determine the imitability of a resource:
The goal is to identify resources that have strong barriers making imitation expensive, time-consuming, or impossible. Without protections, competitors can quickly copy innovations and erode uniqueness.
Finally, VRIO analysis investigates whether an organization is structured, equipped, and ready to fully leverage the valuable, rare, and costly-to-imitate resources identified. Even with secure competitive advantages, they mean little if systems and processes don't capitalize on them.
Assessing organization involves ensuring:
Organization strength means companies can rapidly respond to market changes while fully utilizing resources for maximum value and advantage. It's the last piece connecting internal resources to external strategic applications.
Now, let’s discuss the analysis process to activate these concepts in your business:
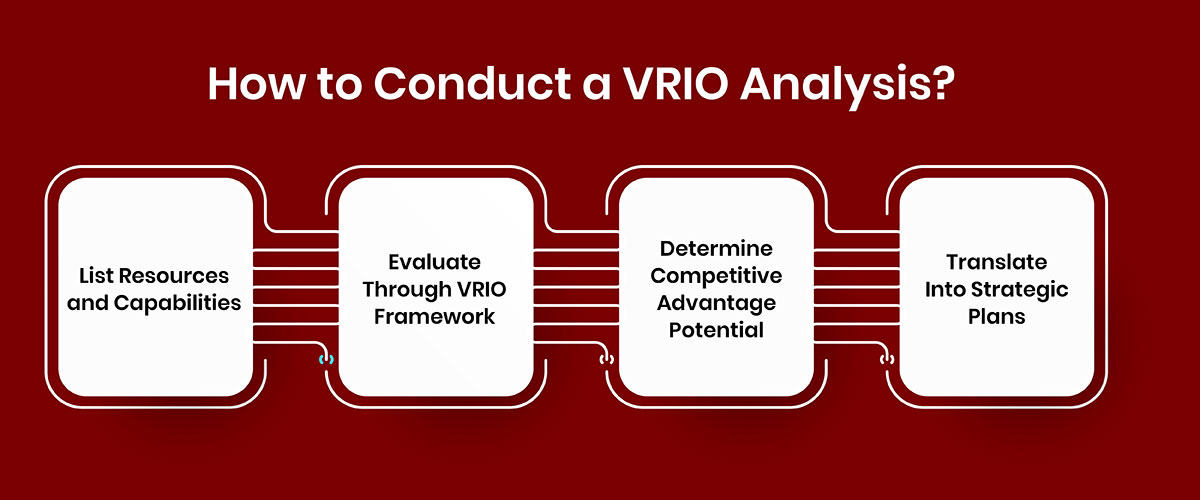
Start by brainstorming an exhaustive list of your resources and capabilities, including:
Next, categorize each resource and capability based on the 4 VRIO criteria questions:
Based on the VRIO assessment, group resources into 4 buckets:
Any resources fitting in groups 1 or 2 likely don’t provide an advantage. They should be low priority areas or candidates for process improvement initiatives.
Resources in groups 3 and 4, however, indicate strategic assets worthy of protection and investment. Focus efforts here to maximize your competitive positioning.
Lastly, build out action plans to leverage resources with the most advantage potential while addressing any gaps or deficiencies uncovered. Use VRIO insights to directly inform executive decision-making, objective setting, budget allocation, and more.
VRIO analysis produces the most value when put into action. Let’s explore a few examples across different industries:
Everyday Low Pricing Model
Through VRIO analysis, Walmart determined its EDLP model enables competitive advantages, including:
By leveraging VRIO insights around its pricing model, Walmart reinforced EDLP as a core competitive advantage to guide strategy.
Distribution Network
Amazon analyzed its distribution capabilities through VRIO:
These VRIO findings led Amazon to continue aggressively investing in supply chain and logistics innovation.
Brand Equity
Coca-Cola used VRIO to assess its brand:
VRIO analysis solidified brand equity and loyalty as a crown jewel competitive advantage directing strategy.
As demonstrated, VRIO offers business leaders an approach to identify differentiating resources that guide plans and growth initiatives.
VRIO and SWOT analysis are two integral strategic planning tools that offer valuable insights into an organization, but take different approaches.
In most cases, conducting a SWOT analysis first to understand the full strategic landscape then using VRIO to detail internal advantages can provide immense value.
Mastering the VRIO strategy framework empowers organizations to sustain strategic positioning even as markets and technology disrupt industries. But remembering VRIO isn’t enough—you must apply these principles to guide objective-setting, investments, partnerships, and operations.
By determining what unique resources provide true advantages, leaders can focus efforts in the right areas. Pair VRIO with execution tools like OKRs to translate insights into tangible growth.

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.